Data intensive applications
“big data”
first and foremost: principle 1: Security is everyone’s responsibility
12 Factor
A methodology for building software-as-a-service apps
- Codebase
- Dependencies
- Config
- Backing services
- Build, release, run
- Processes
- Port binding
- Concurrency
- Disposability
- Dev/prod parity
- Logs
- Admin processes

Hadoop history
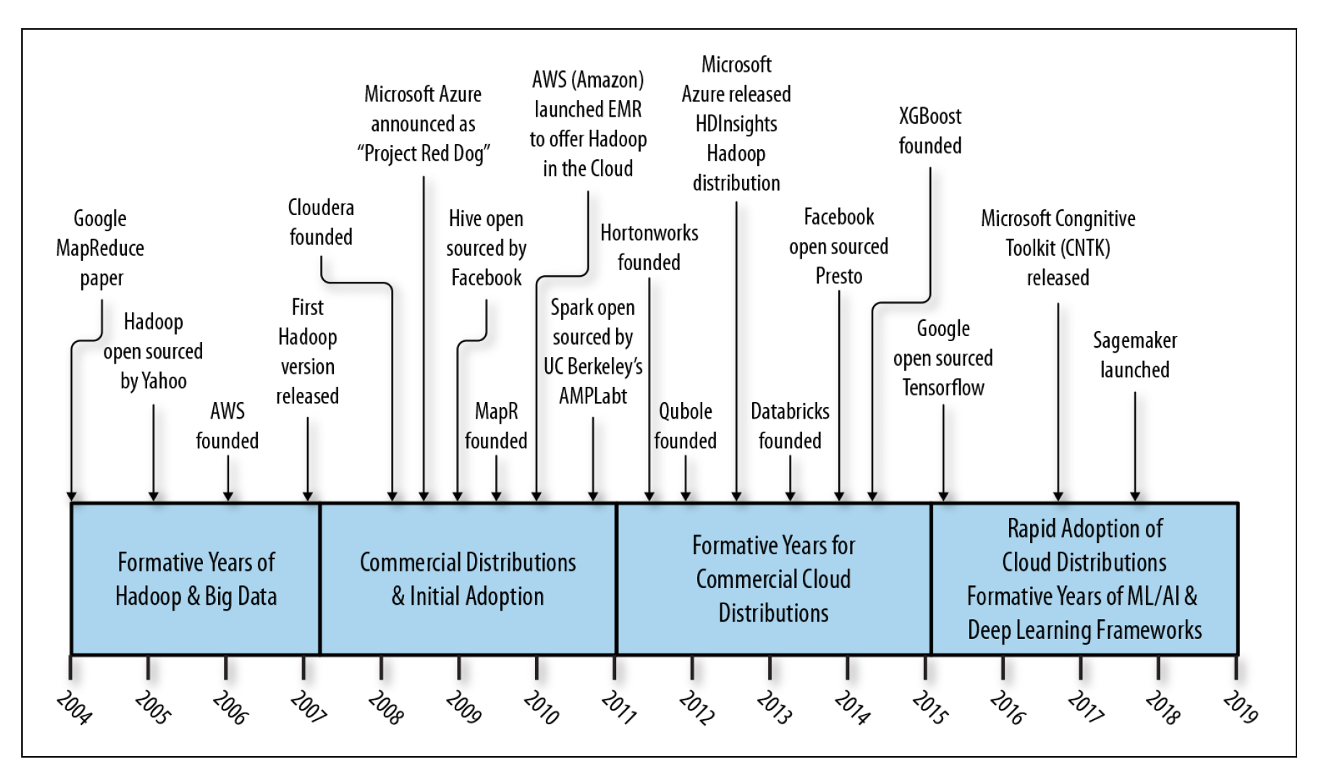
Hadoop at pinterest
Large Scale Hadoop Upgrade At Pinterest
- Pinterest’s Batch Processing Platform, Monarch, consists of more than 30 Hadoop YARN clusters with 17k+ nodes built entirely on top of AWS EC2.
- At the beginning of 2021, Monarch was still on Hadoop 2.7.1, which was already five years old. Because of the increasing complexity in backporting upstream changes (features and bug fixes), we decided it was time to invest in a version upgrade.
Analytics - data solutions - history
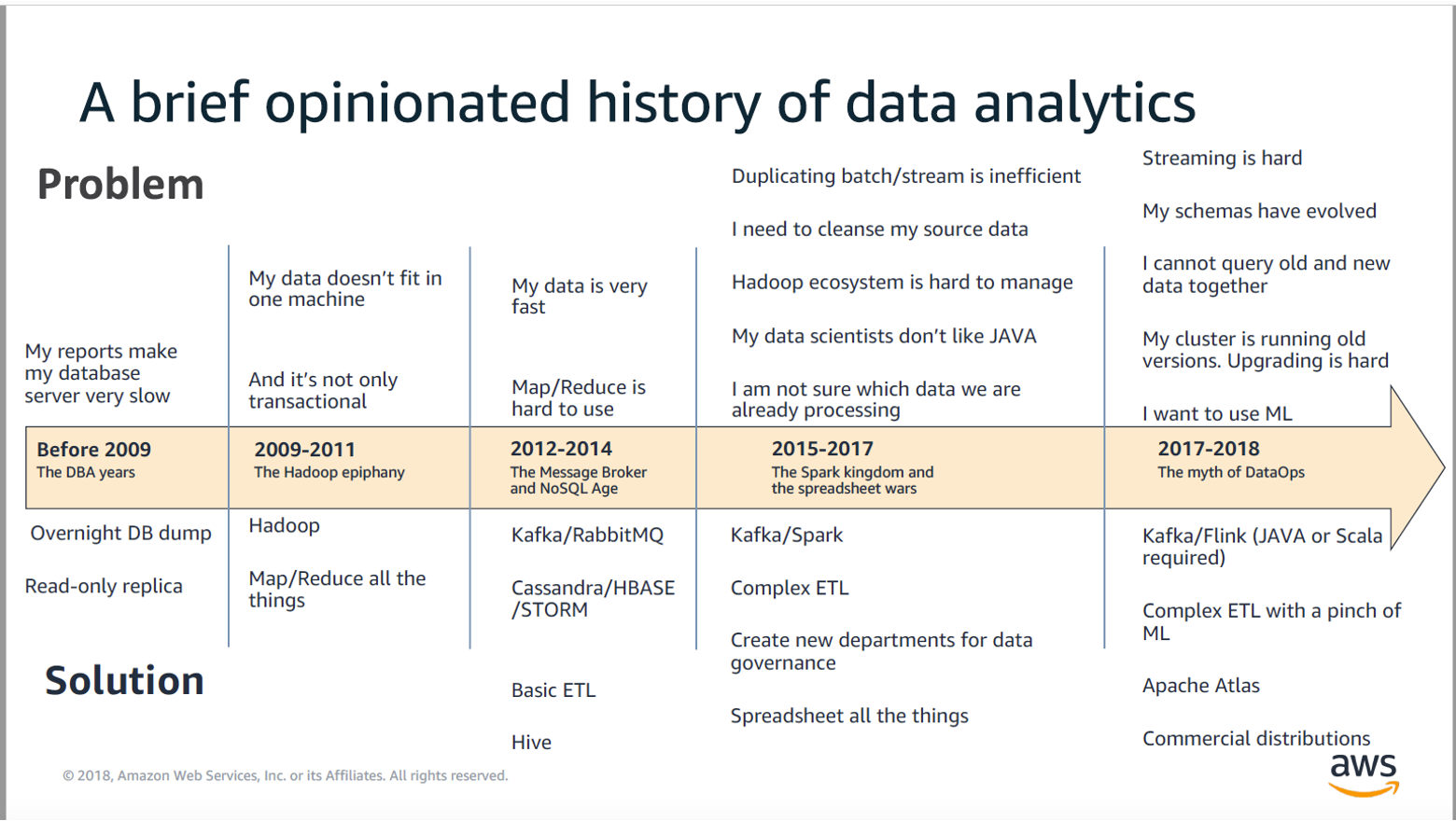
Transaction processing or analytics
OLTP - OLAP, on the surface both looks equal, they offer SQL
| OLTP | OLAP | |
|---|---|---|
| read pattern | small number of records, fetch per key | aggregate large volumes |
| write pattern | random access, low latency writes | bulk import, or stream events |
| primary use | end-user | decision support |
| type of data | latest state of data, current point int time | history of events |
| size |
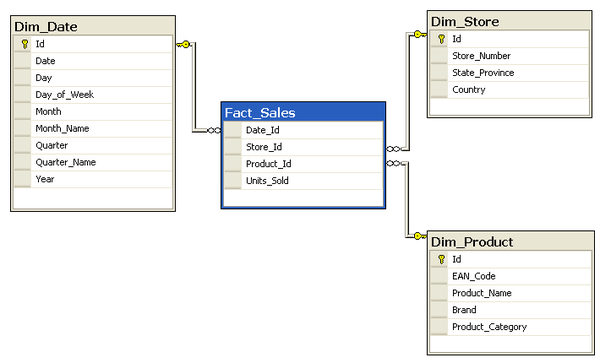
Data models for analytics
Star schema, dimension and fact tables
SELECT
P.Brand,
S.Country AS Countries,
SUM(F.Units_Sold)
FROM Fact_Sales F
INNER JOIN Dim_Date D ON (F.Date_Id = D.Id)
INNER JOIN Dim_Store S ON (F.Store_Id = S.Id)
INNER JOIN Dim_Product P ON (F.Product_Id = P.Id)
WHERE D.Year = 1997 AND P.Product_Category = 'tv'
GROUP BY
P.Brand,
S.Country
Snowflake schema
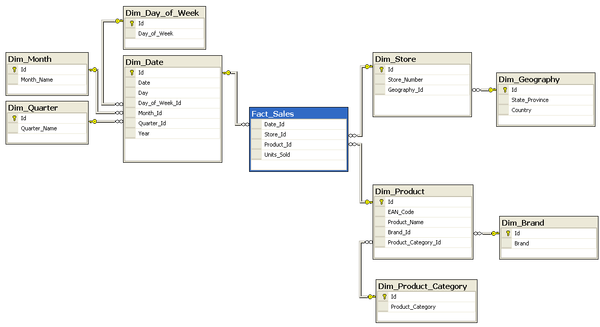
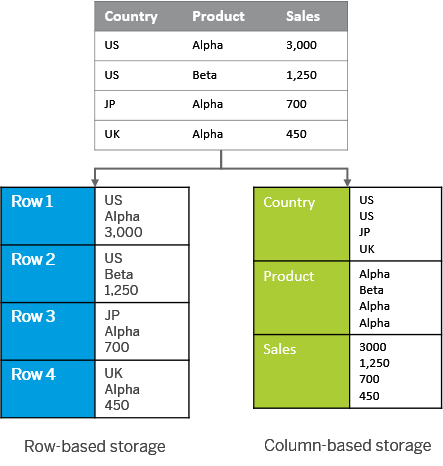
Column oriented storage
By default, OLTP systems is storing data in row store oriented databases.
For OLAP, colum store is much more adapted to the query patterns.
Column-oriented storage, store each column in a sorted file. That makes it easy to apply a compression on it.
First, second and third generation data platforms
How to Move Beyond a Monolithic Data Lake to a Distributed Data Mesh
lambda
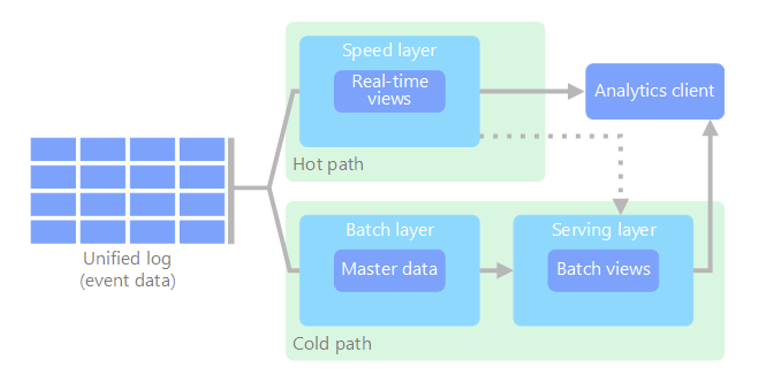
Two paths for data flow. All data coming into the system goes through these two paths
- a batch layer, cold path, stores all of the incoming data in its raw form and performs batch processing on the data. The result is stored as a batch view
- a speed layer, hoth path, analyzes data in real time. This layer is designed for low latency, at the expense of accurancy
kappa
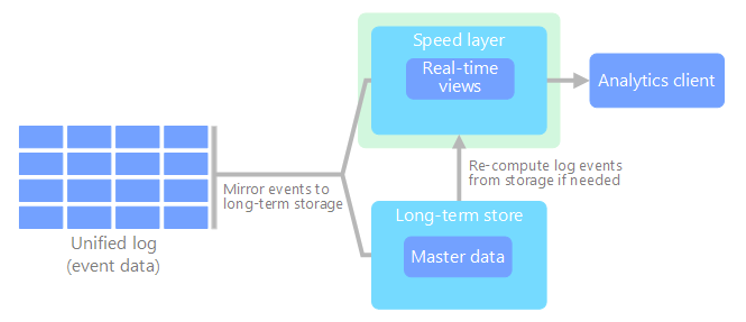
An alternative to the lambda architecture. It has the same basic goals as the lambda architecture. but with an important distinction: all data flows through a single path, using a stream processing system
3V’s
Hadoop
HDFS + Yarn + a collection of jars …
A bold statement: “Hadoop opened the philosophy to dump data into HDFS and only make sense of it later” By contrast to data warehouses that requires upfront modelling
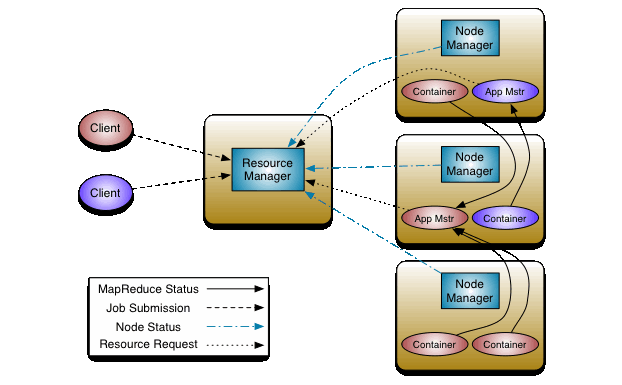
Hadoop YARN
Resource management and scheduling + monitoring of applications
Replication and partitioning
Shared nothing architecture, horizontal scaling - scaling out
Each machine running the (database) software is called a node.
Each node has it’s own CPU, RAM, HDs.
replication
Keeping a copy of the same data on several nodes –> redundancy
partitioning
Splitting a big database/dataset into smaller subsets called partitions, so that different partitions can be assigned to different nodes
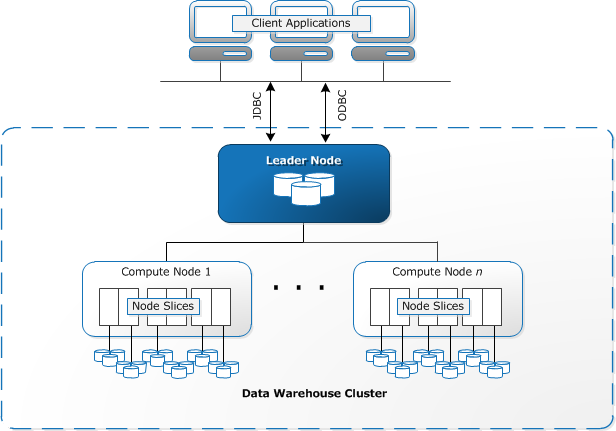
Redshift nodes
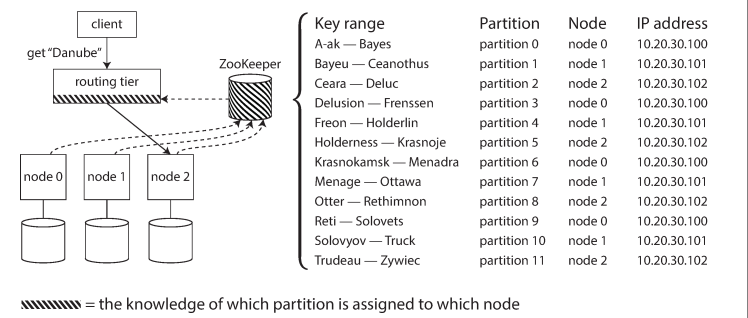
Request routing - service discovery
Where are is the data now, on which node?
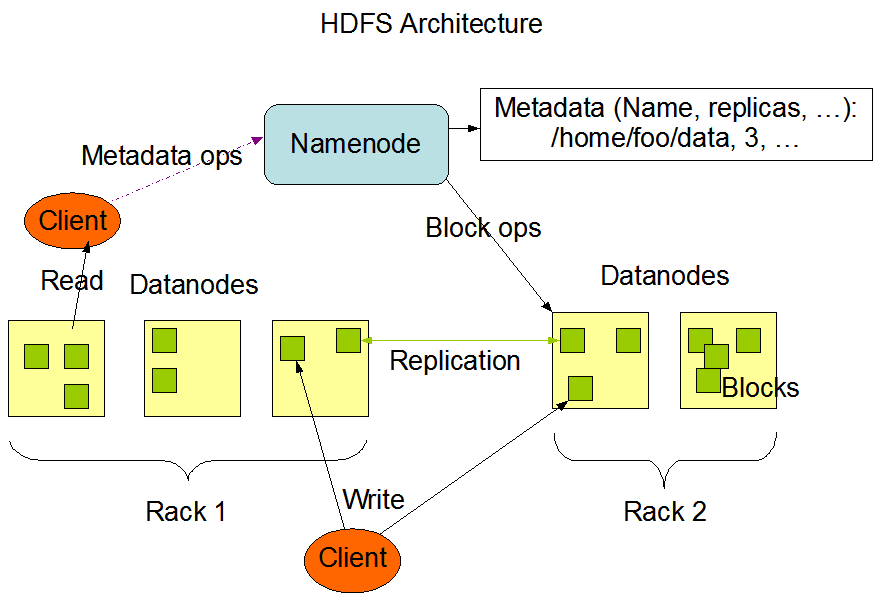
HDFS
- Primary storage system for Hadoop: it stores large files in small blocks (128 MB)
- Designed to be deployed on low-cost hardware
- Designed to scale easily and effectively
- Reliability: data is replicated so that disk fail over is not only acceptable but expected and handled seamlessly
HDFS nodes
MapReduce
Published in 2004, a low level programming model. Unable us to write code over large datasets
-
MAP TASK purpose: main purpose is to READ ALL DATA
-
Goal: is to achieve data locality
-
EACH reducer asks EACH mapper for the key/value pairs designated for that reducer -> partitioning
-
EACH reducer reads its key/value pairs, the values are aggregated into a collection and the entire input to the reducer is SORTED by keys. The shuffle/sort phase
-
The REDUCE typically business logic
-
IF you have X reducers, you will have X result files
MPP
- An MPP database focuses on // execution of analytical SQL queries
- MapReduce is a general-purpose processing framework
Teradata exists from a long time before MapReduce
Hive
-
Is not a database, but uses a database (called metastore) to store the tables you define
-
A Hive table contains of a schema stored in the metastore and data stored in HDFS (or s3, or ADL or …)
-
Hive converts HIVESQL commands to mapreduce jobs (or Tez …)
-
HIVESQL is similar to SQL
Spark
A unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing
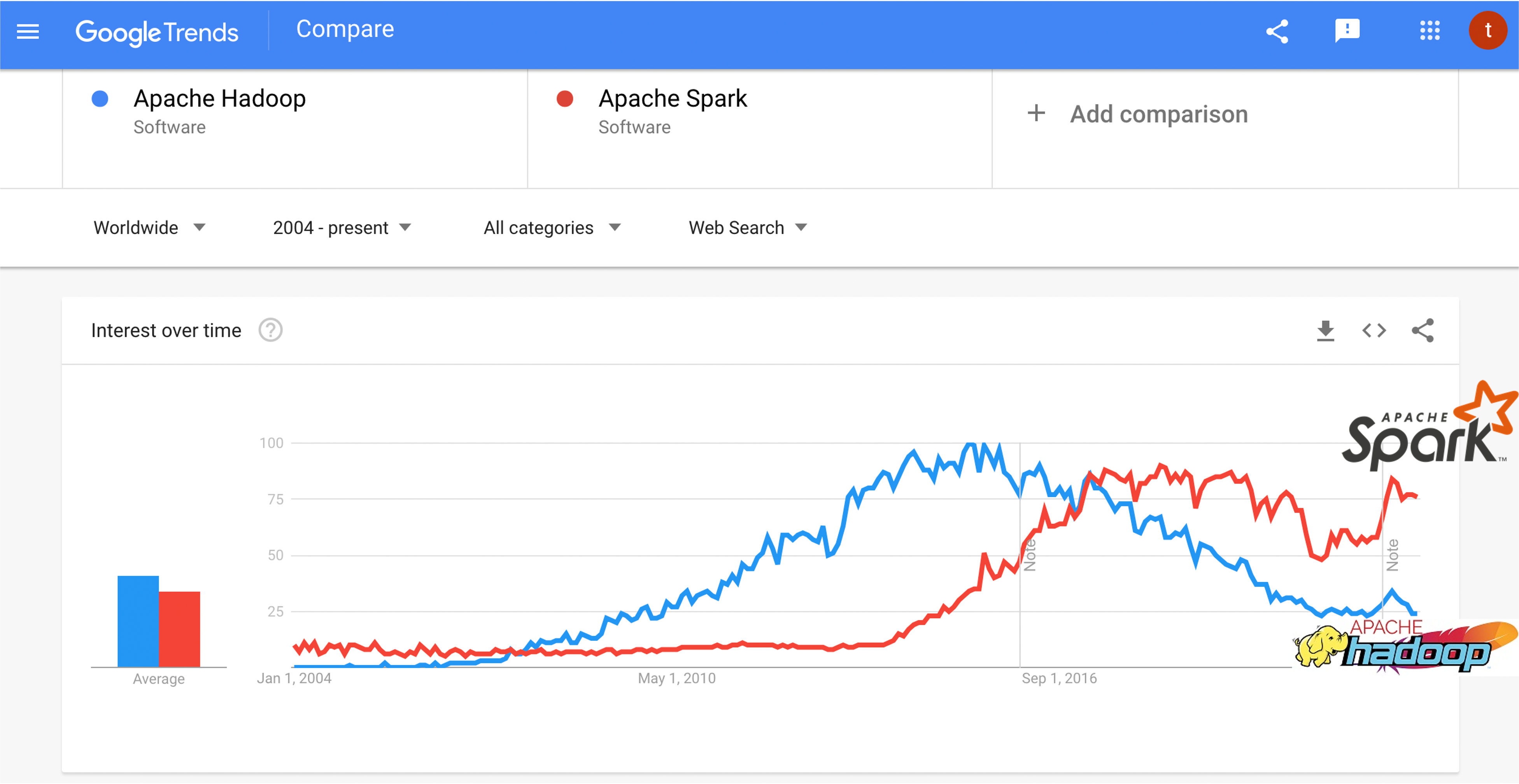
Spark also being the foundation for
- https://hudi.apache.org/ a transactional data lake platform
- https://delta.io/ an open-source storage framework that enables building a Lakehouse architecture
- https://iceberg.apache.org/ The open table format for analytic datasets
GitHub Codespaces
GitHub Codespaces
4 core / 8GB vm costs: $ 0.36 / hour
AWS has in preview CodeCatalyst: https://codecatalyst.aws/explore/dev-environments 4 vCPU / 8GB costs: $0.23/hour + $0.01/min
GitHub Codespaces
We are running in the cloud on Ubuntu and docker is installed
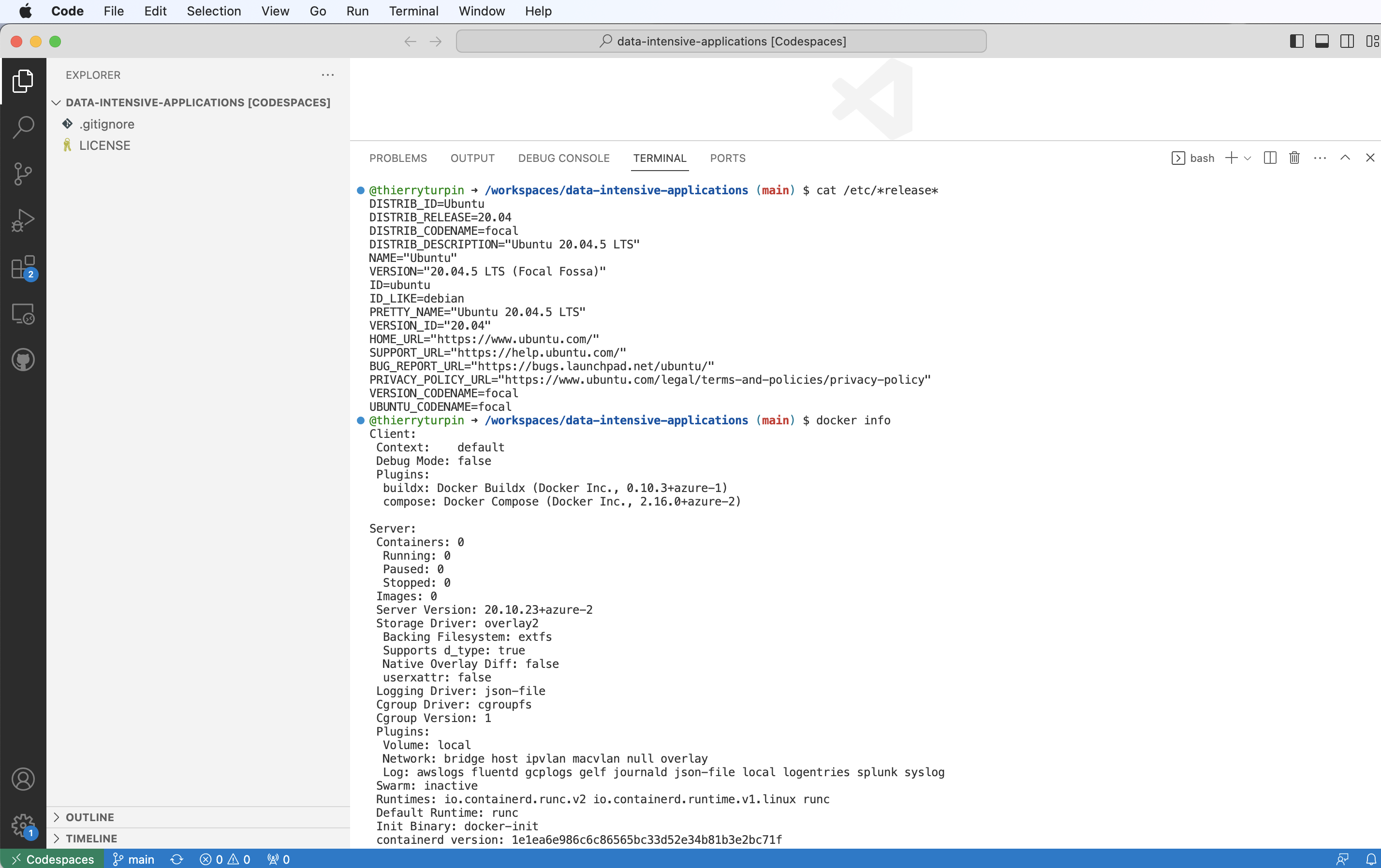
Why docker?
It worked on my machine!
- Exact reproducible environments - immutable --> stability!
- lightweight
- Ease to ship, package and ship anything, in a uniform way!
- Ease of use
- Workload isolation
Docker
Mastering docker is a must for data engineering
- Many vendors package applications that you can deploy in minutes under docker, examples:
Mastering docker is the first step towards k8s
Docker desktop?
Docker Desktop is licensed as part of a free (Personal) or paid Docker subscription (Pro, Team or Business).
Docker Desktop may be used for free as part of a Docker Personal subscription for:
- Small companies (fewer than 250 employees AND less than $10 million in annual revenue)
- Personal use
- Education and learning (as a student or an instructor, either in an academic or professional environment)
- Non-commercial open source projects
Rancher desktop or podman
Container Management and Kubernetes on the Desktop
An open-source desktop application for Mac, Windows and Linux. Rancher Desktop runs Kubernetes and container management on your desktop. You can choose the version of Kubernetes you want to run.
Comparing to Virtual machines
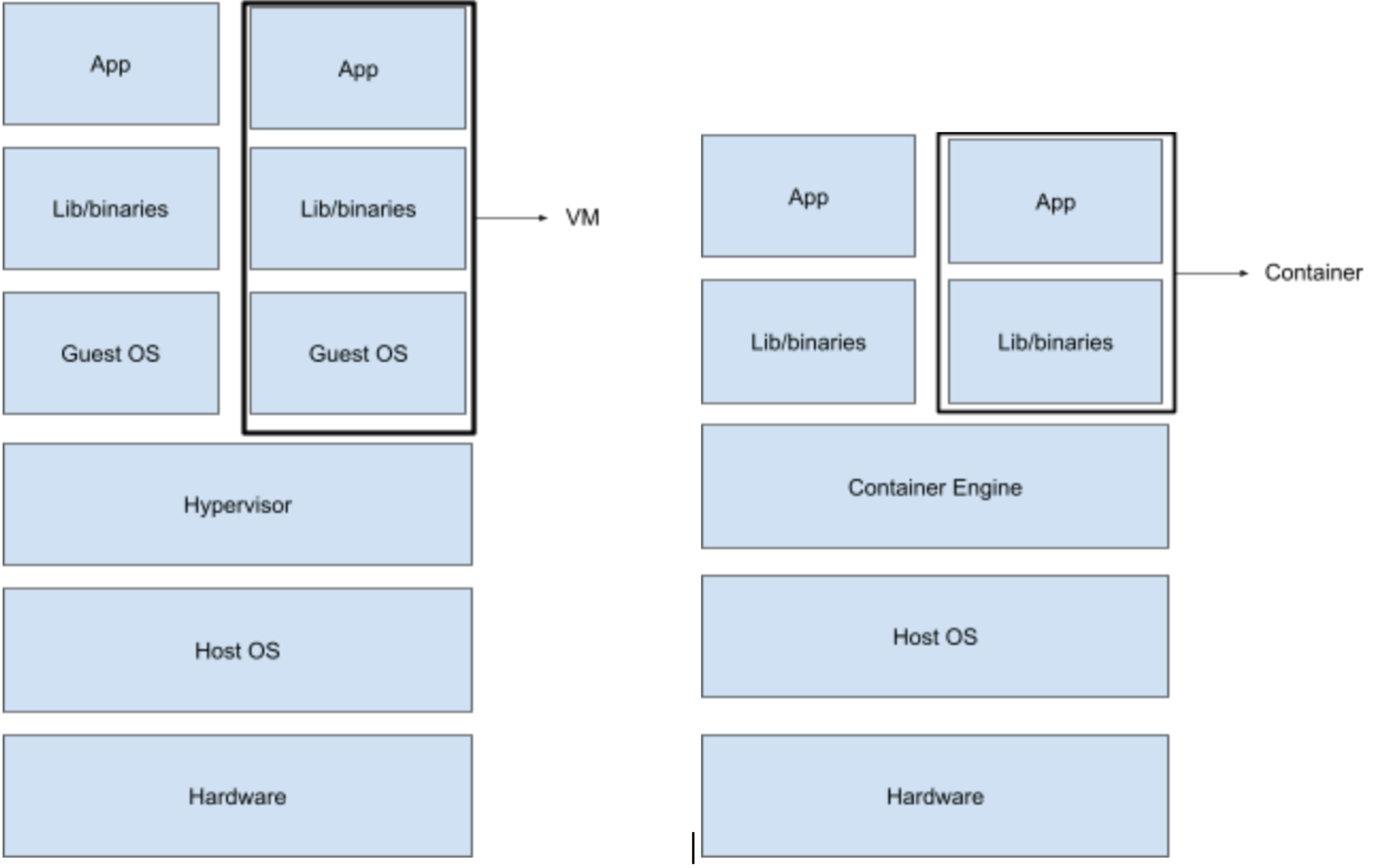
Native processes - on linux
docker run -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=SuperSecure -d public.ecr.aws/docker/library/postgres:latest
@thierryturpin ➜ /workspaces/data-intensive-applications (main) $ docker run -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=SuperSecure -d public.ecr.aws/docker/library/postgres:latest
Unable to find image 'public.ecr.aws/docker/library/postgres:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from docker/library/postgres
7a6db449b51b: Pull complete
b4f184bc0704: Pull complete
606a73c0d34a: Pull complete
c39f1600d2b6: Pull complete
31f42f92b0fe: Pull complete
c8b67d2b0354: Pull complete
31107b8480ee: Pull complete
b26434cf8bfa: Pull complete
36220bd76bfa: Pull complete
b79e75c4a0c2: Pull complete
cc1ab699dda5: Pull complete
37312064dd9b: Pull complete
4bce56fcbfe5: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:befb4cdc1d944bd89784b9caa287cf025f0720f9a02436038124163accd177dc
Status: Downloaded newer image for public.ecr.aws/docker/library/postgres:latest
71e9e6d94fa80c700fc5abbb4ed9600b1fbb026b439e2347ae789f2ae933e215
Native processes - on Linux
@thierryturpin ➜ /workspaces/data-intensive-applications (main) $ pstree
docker-init─┬─containerd-shim─┬─postgres───6*[postgres]
│ └─10*[{containerd-shim}]
├─dockerd─┬─containerd───8*[{containerd}]
│ ├─2*[docker-proxy───5*[{docker-proxy}]]
│ └─11*[{dockerd}]
├─sleep
└─sshd
Docker file - images - containers
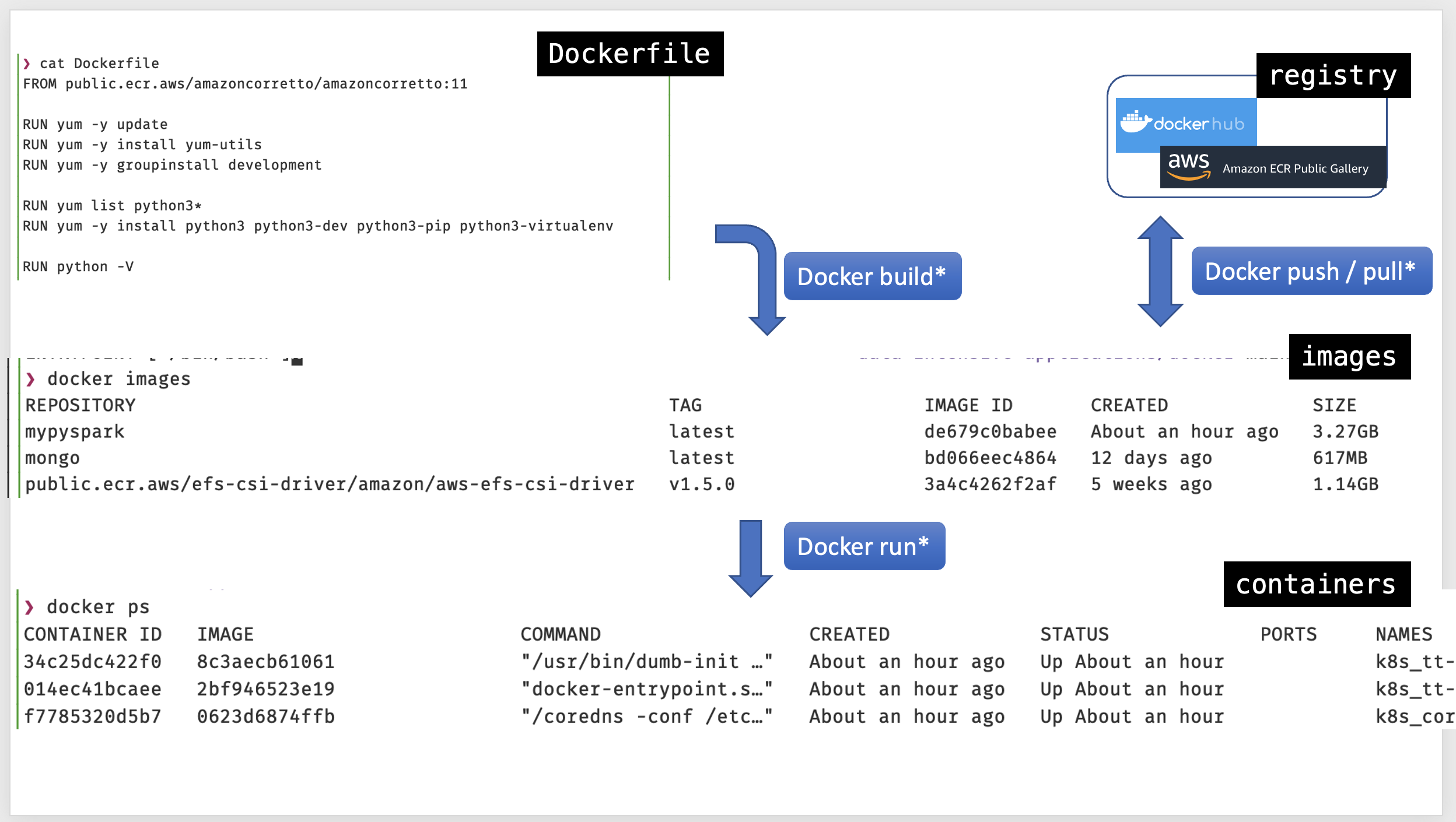
Docker
Where are we now?
cat /etc/*release*
Is docker installed
docker -v
Do we have docker-compose?
docker-compose -v
Let’s run our first container
docker run -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=SuperSecure -d public.ecr.aws/docker/library/postgres:latest
-pport forwardhost:container-eset’s the environment variablePOSTGRES_PASSWORDinside the container-drun the container is detached mode (background)public.ecr.aws/docker/library/postgres:latestthe docker image
Check the running container(s)
docker ps
Note your container ID (we didn’t named it)
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
e22abdc669c2 public.ecr.aws/docker/library/postgres:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp, :::5432->5432/tcp sleepy_snyder
Shell into the container 1/2
Replace your container ID
docker exec -it e22abdc669c2 bash
root@e22abdc669c2:/#
cat the release files
root@e22abdc669c2:/# cat /etc/*release*
PRETTY_NAME="Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye)"
NAME="Debian GNU/Linux"
VERSION_ID="11"
VERSION="11 (bullseye)"
VERSION_CODENAME=bullseye
ID=debian
HOME_URL="https://www.debian.org/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://www.debian.org/support"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.debian.org/"
root@e22abdc669c2:/#
Shell into the container 2/2
exit the container
root@e22abdc669c2:/# exit
exit
Check the Postgres database
Install a Postgres client, example CLI client psql
Update packages
sudo apt-get update
Install client
sudo apt-get install -y postgresql-client
Connect to the database
psql -h localhost -d postgres -U postgres
Password for user postgres:
psql (12.12 (Ubuntu 12.12-0ubuntu0.20.04.1), server 14.5 (Debian 14.5-1.pgdg110+1))
WARNING: psql major version 12, server major version 14.
Some psql features might not work.
Type "help" for help.
Use of the Postgres client
to see a list of all tables use \dt *.*
to check the users created in the db, query table pg_user
postgres=# \dt *.*
postgres=# select * from pg_user;
usename | usesysid | usecreatedb | usesuper | userepl | usebypassrls | passwd | valuntil | useconfig
----------+----------+-------------+----------+---------+--------------+----------+----------+-----------
postgres |
to quit use \q
postgres=# \q
@thierryturpin ➜ /workspaces/data-intensive-applications (main) $
There’s more
docker logs e22abdc669c2 -f
CTRL C to stop following the log
Get the details with inspect
docker inspect sleepy_snyder
[
{
"Id": "e22abdc669c2622b87f0489fdcbcff2676803d9bc05114bae141d71d268123b1",
"Created": "2022-08-26T08:21:18.697009815Z",
"Path": "docker-entrypoint.sh",
"Args": [
"postgres"
],
"State": {
"Status": "running",
"Running": true,
"Paused": false,
"Restarting": false,
"OOMKilled": false,
"Dead": false,
"Pid": 5438,
"ExitCode": 0,
"Error": "",
"StartedAt": "2022-08-26T08:21:19.119424024Z",
"FinishedAt": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
...
Kill the running container
docker kill e22abdc669c2
Nice, how do persist data, run multiple containers…
Create a docker image for Spark and MongoDB
cd docker
Let’s build a docker image named mypyspark based on the file Dockerfile
docker buildx build -t mypyspark .
Note the Dockerfile has 16 layers
Verify which docker images we have
docker images
Image name, tag and digest
- name, the thing needs to be named
- tags refer to a version, tags are mutable
- digest, are immutable, sha-256 or sha-512 of the layers information
Anatomy of the Dockerfile
First line, we start from amazoncoretto a production-ready distribution of the Open Java Development Kit.
Spark requires JAVA.
FROM public.ecr.aws/amazoncorretto/amazoncorretto:11
If we only intend to use the PySpark api, since Spark 2.2 we can install it as a Python package.
last line of the requirements/requirements.txt file
pyspark==3.1.2
Get Data from s3 - transform - store into mongoDB
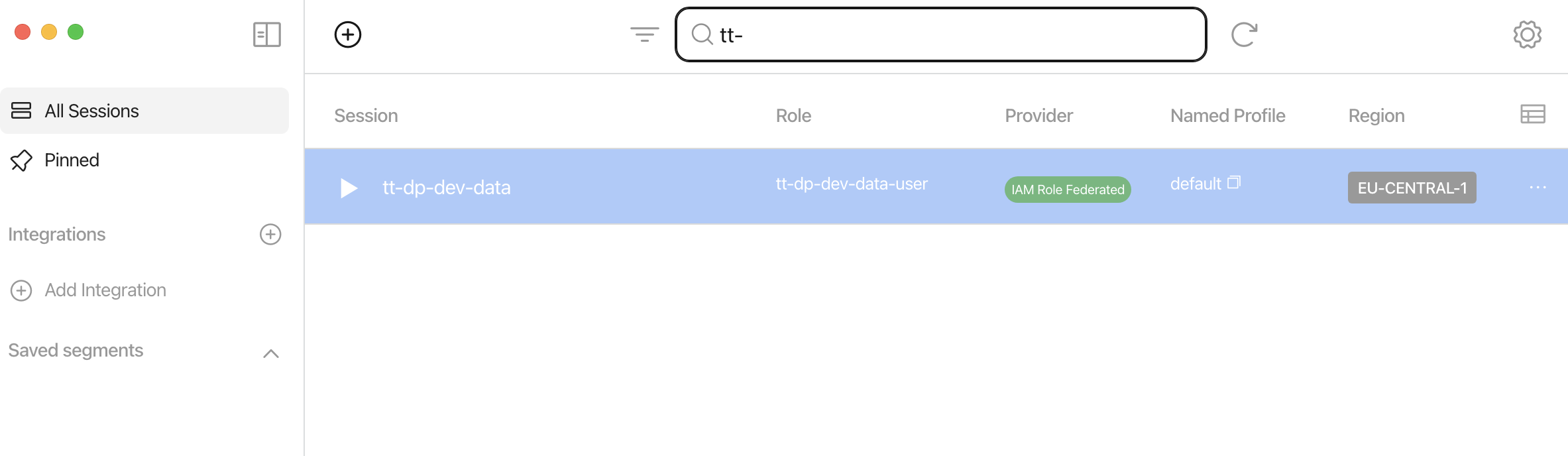
AWS user keys should be the last resort
The AWS account has been integrated with auth0 Identity Provider (IDP)
Doing so we limit the number of AWS IAM users to be managed in the AWS account.
Generate STS credentials with Leapp
Create a profile with the parameters in the file README.md
Execute Pyspark 1/3
On the host, start docker-compose in detached mode
the .env file is used by docker-compose to set mongodb credentials
example of the .env file:
export MONGODB_USERNAME=training
export MONGODB_PASSWORD=training
cd docker
source .env
docker-compose up -d
This will:
- pull the official docker image for mongodb
- run the mongodb and PySpark containers
- run mongodb init scripts to create the extra db and set grants
- expose ports
Execute Pyspark 2/3
On the host, start a docker shell
Update your AWS keys (lines 3,4 and 5) in the file docker/code/docker-exec-with-aws-keys.sh
source the docker-exec-with-aws-keys.sh to start a shell into the mypyspark container passing AWS credentials
cd code
source docker-exec-with-aws-keys.sh
Execute Pyspark 3/3
In the container start python3 PySpark
- The host
codedirectory is mapped tooptinside the container - The
.envfile contains the variables for Pyspark to connect to MongoDB
example of the .env file:
export host=mongo
export user=training
export password=training
export database=dev
The Pyspark script takes in input a single parameter, the s3 path to the races.csv file
cd /opt/
source .env
python3 s3_to_mongo.py --s3_path=s3://tt-dp-dev-datalake/formula1/races.csv
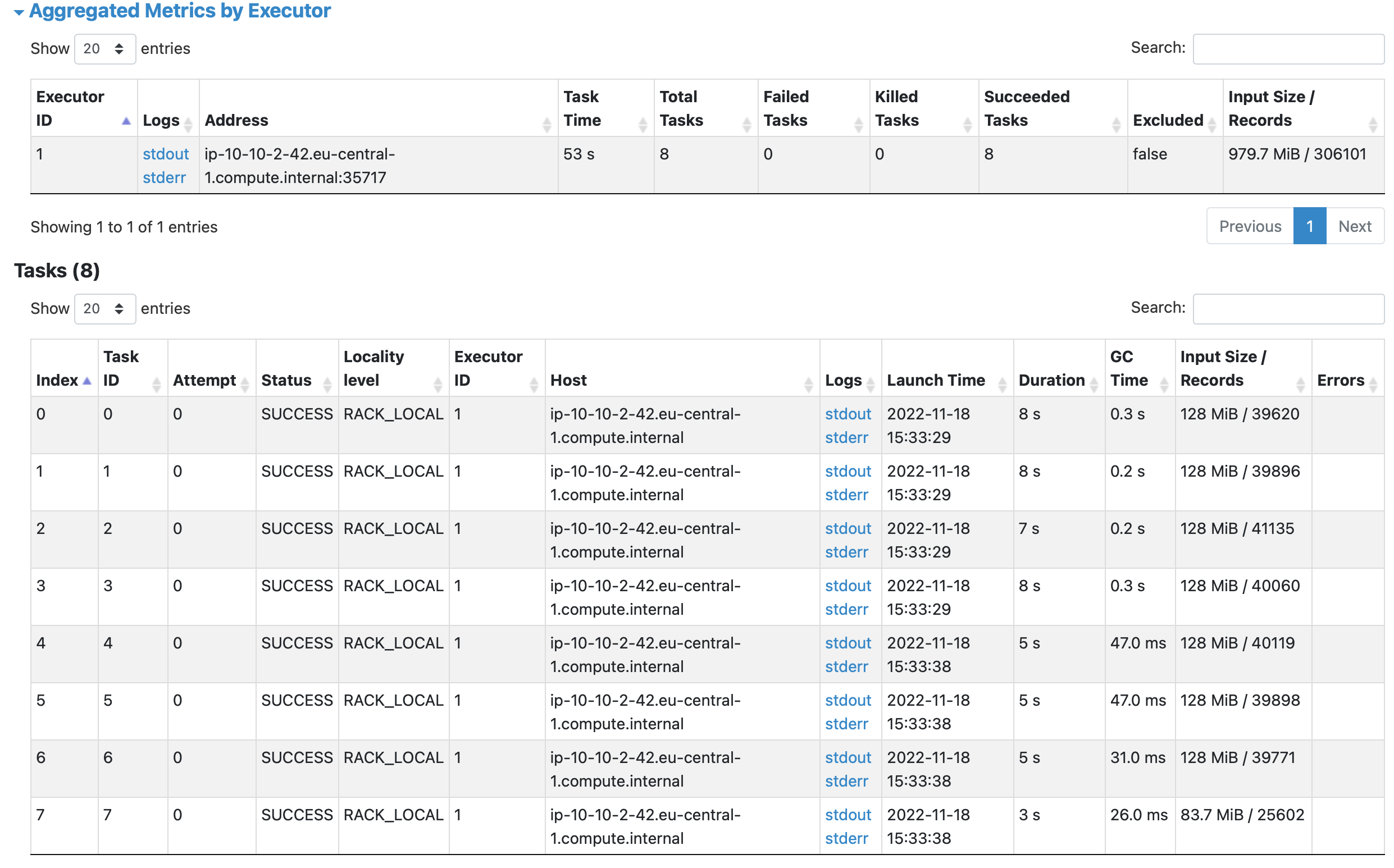
Check the Spark History UI
Is exposed via the port mapping done in the docker-compose.yml file
pyspark:
container_name: mypyspark
image: mypyspark
ports:
- "8080:4040"
Spark Jobs - Stages - Tasks & Partitions
Jobs, a job breaks down in a series of stages (a DAG)
Stage groups of tasks that can be executed together
Partition represents how the data is physically distributed during execution
Shuffles a physical repartition of the data
Dataframes
In contrast to a “normal” Python dataframe, a Pyspark Dataframe can span different machines
Input file split
Verify the data using the mongoshell
on the host
Install the package
wget https://downloads.mongodb.com/compass/mongodb-mongosh_1.0.5_amd64.deb
sudo apt-get install ./mongodb-mongosh_1.0.5_amd64.deb
Establish a connection
mongosh mongodb://localhost:27017/dev -u training
Show collections, this should list the races collection
dev> show collections
Find records, will return the filtered dataframe records
dev> db.races.find()
Spark cluster mode
Besides the standalone mode, it can run on a Cluster
A custer managed by, YARN or Kubernetes
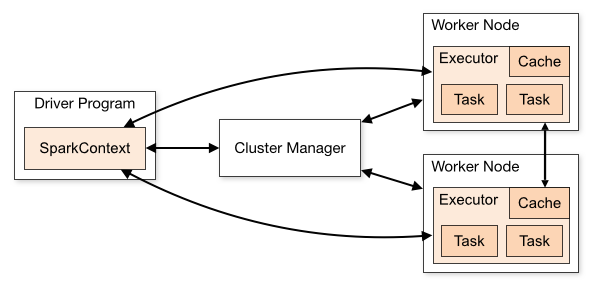
- Spark driver
- initiates a Spark Session (Spark context)
- requests resources from the cluster manager
- Executor, on each worker node and executes the tasks
spark-submit
spark-submit does 1 thing: it lets send your code to a cluster
example:
spark-submit --master yarn --deploy-mode client twitter.py
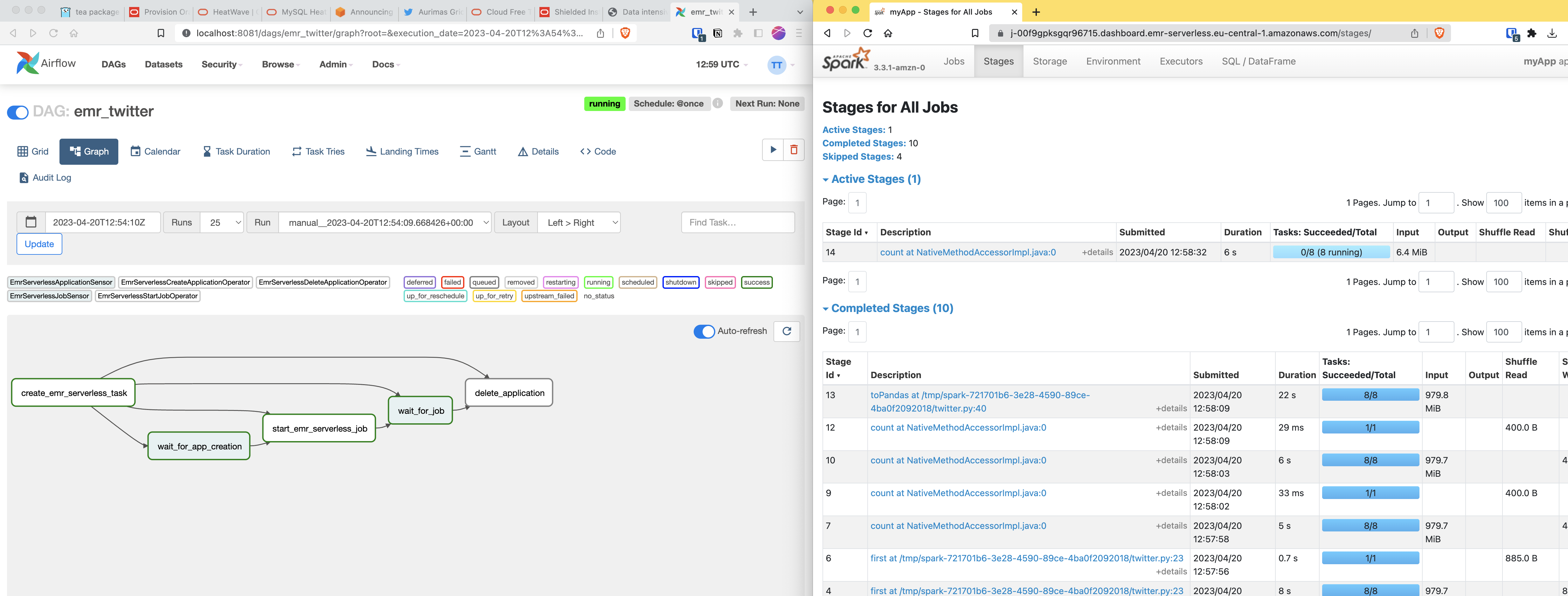
AWS Elastic Map Reduce (EMR)
AWS EMR has some additional pattern capabilities compared to traditional clusters
- Cluster are created per and for a specific workload, scaled and optimized for the workload
- Yarn is a resource negotiator and workload orchestrator, EMR adds a external addressable **steps** notion on top
- EMR steps can be used to monitor and sense the workload, and also to **terminate** a cluster on task completion
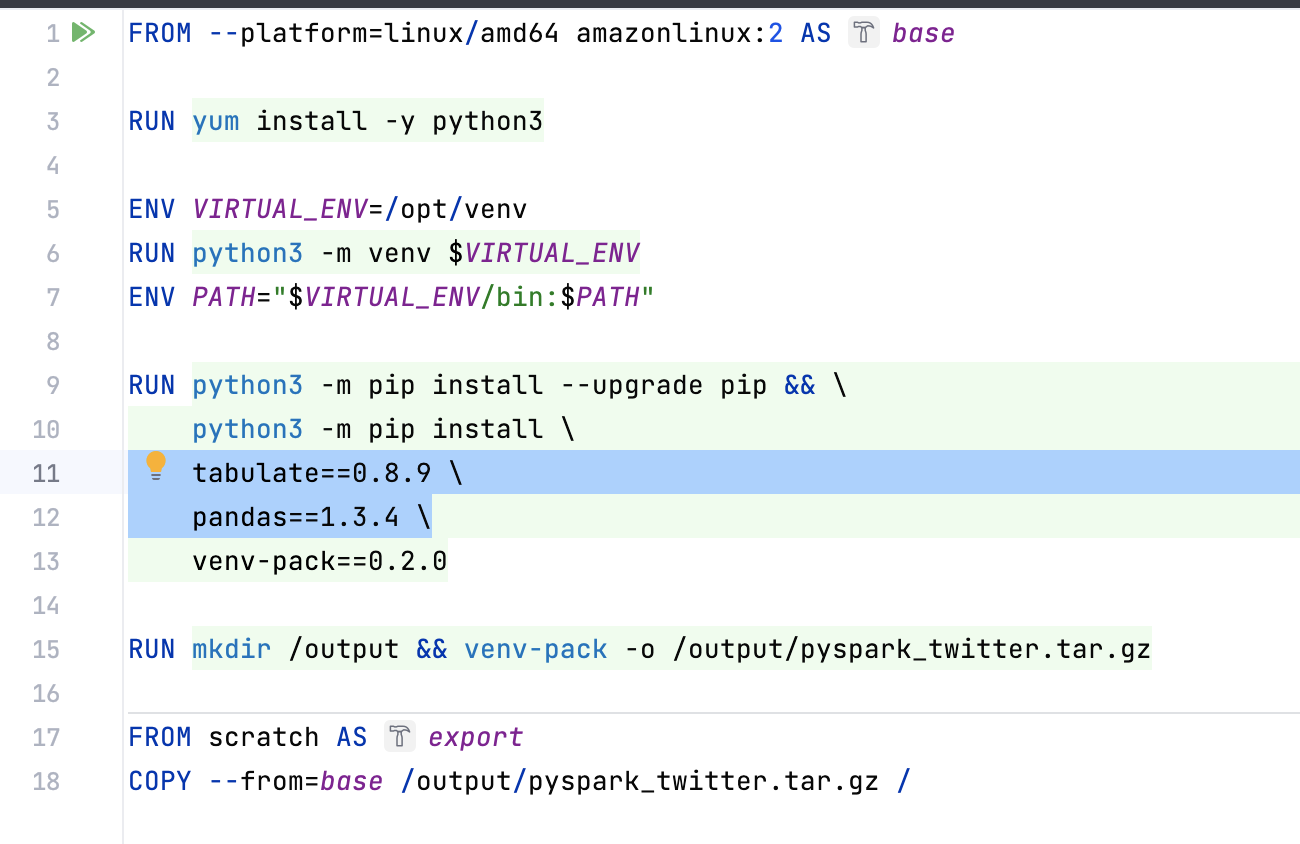
EMR serverless
EMR serverless can use python venv to package your python libs
This needs to be done on amazonlinux 2
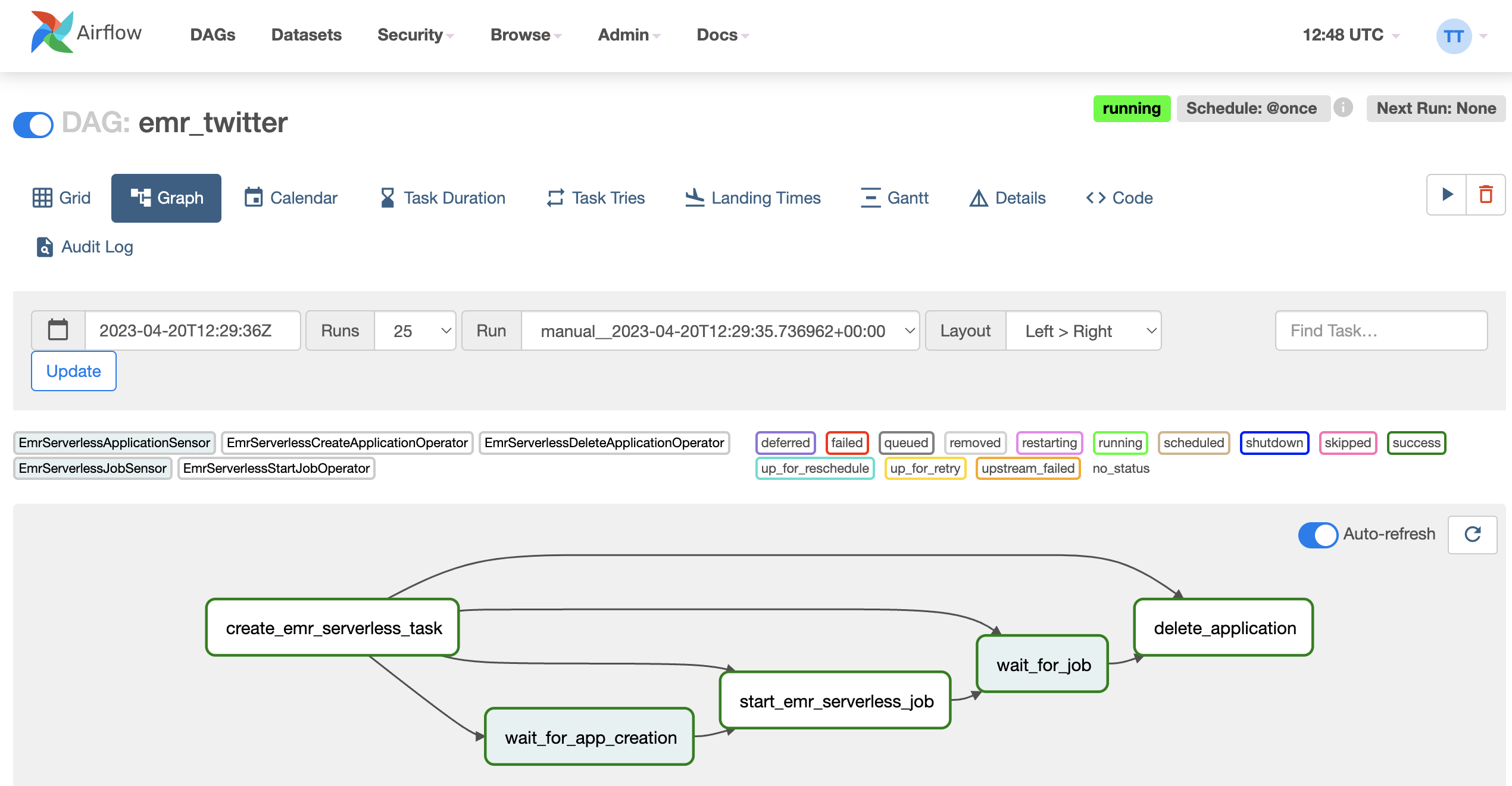
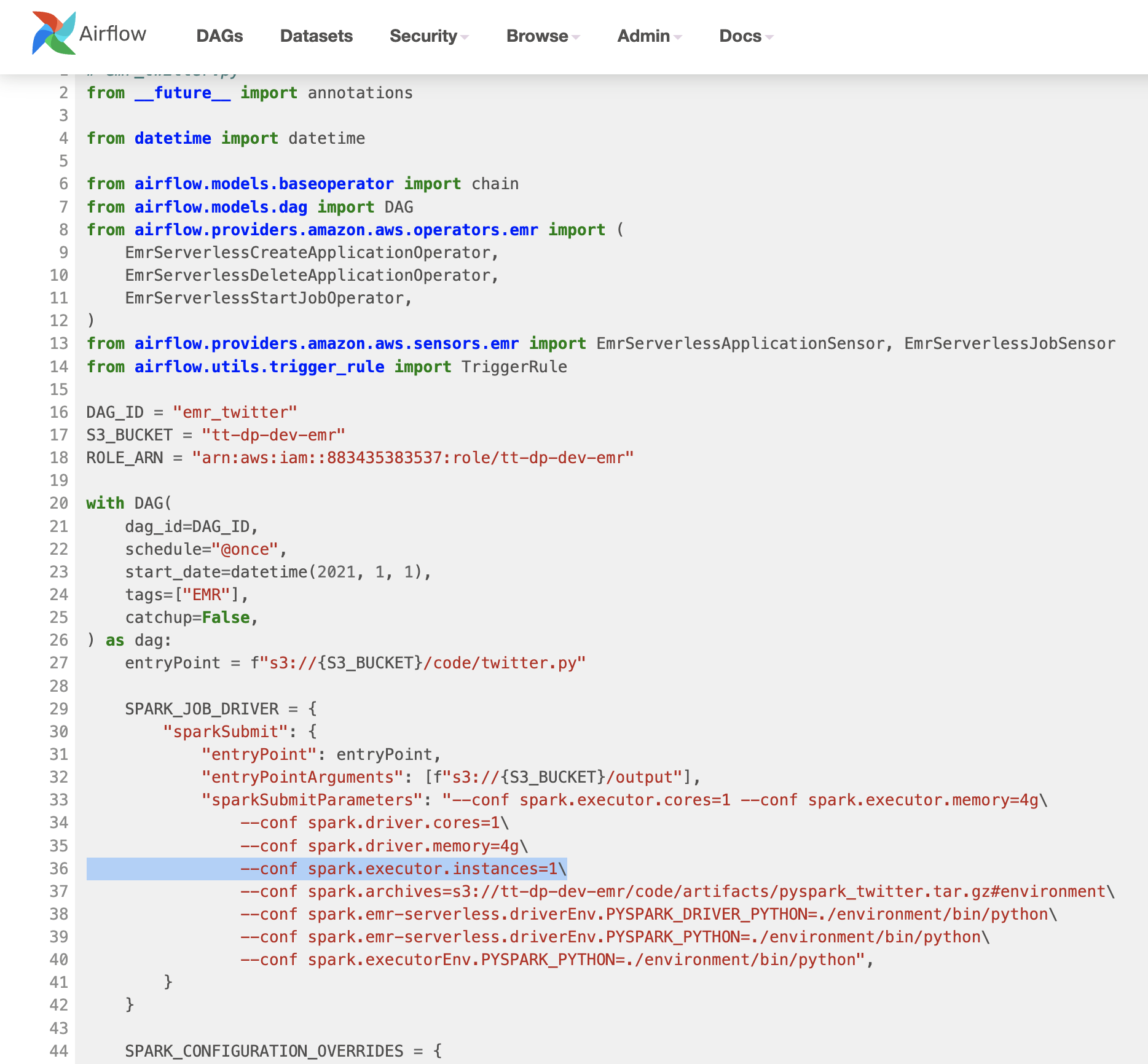
EMR serverless via Airflow
Stay up to date !